Psychiatry vs Psychology: Understanding the Key Differences
Delving into Psychiatry vs Psychology: Understanding the Key Differences, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative that explores the distinctions between these two fields. From defining psychiatry and psychology to highlighting their differences in approach and education, this overview sets the stage for an enlightening discussion.
As we delve deeper into the nuances of these disciplines, a clearer picture emerges of how psychiatrists and psychologists navigate the realm of mental health with distinct methodologies and expertise.
Psychiatry vs Psychology
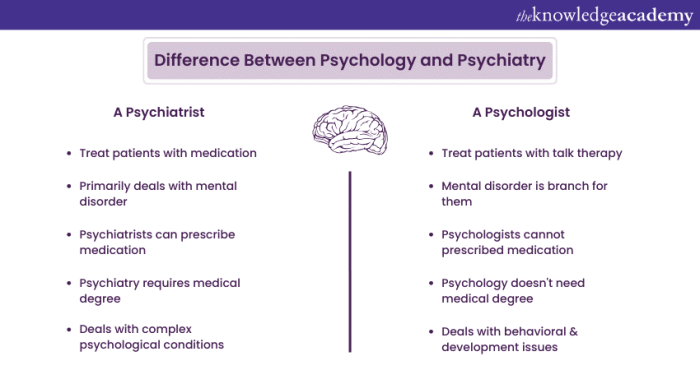
Psychiatry and psychology are both fields focused on mental health, but they differ in their approaches and practices. Psychiatry is a branch of medicine that deals with diagnosing and treating mental illnesses using a medical model, including prescription medications and other medical interventions.
Psychology, on the other hand, is a behavioral science that focuses on understanding human behavior and mental processes through observation, assessment, and therapy.
Primary Differences
- Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medications, while psychologists cannot prescribe medication and mainly use therapy as a treatment approach.
- Psychiatrists often work in hospitals or clinical settings, while psychologists may work in private practice, schools, or research institutions.
- Psychiatrists tend to focus more on the biological aspects of mental health, while psychologists emphasize the psychological and behavioral components.
Approach to Mental Health
- Psychiatrists may use a combination of medication management and therapy to treat mental health disorders, while psychologists primarily use therapy techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or psychotherapy.
- Psychiatrists may use diagnostic tools like brain imaging or lab tests to aid in diagnosis, while psychologists rely on interviews, assessments, and behavioral observations.
Educational Requirements
- Psychiatrists are required to complete medical school, followed by a residency in psychiatry, which usually takes around 12 years of education and training.
- Psychologists typically obtain a doctoral degree in psychology, which can take around 5-7 years of graduate education and supervised experience to become licensed.
Scope of Practice
Psychiatrists and psychologists play distinct roles in the mental health field, each with a defined scope of practice tailored to their specific expertise and training.
Scope of Practice for Psychiatrists
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in mental health. They are trained to diagnose, treat, and prevent mental illnesses through a combination of medication management, psychotherapy, and other interventions. Psychiatrists are licensed to prescribe medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers, to help manage mental health conditions.
Scope of Practice for Psychologists
Psychologists, on the other hand, are mental health professionals with advanced degrees in psychology. They focus on providing psychotherapy, counseling, and behavioral interventions to help individuals cope with emotional and psychological issues. Psychologists do not prescribe medication but work collaboratively with psychiatrists and other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive care for their clients.
Treatment Approaches
- Psychiatrists primarily use a biomedical approach, which involves medication management to address chemical imbalances in the brain that contribute to mental health conditions.
- Psychologists, on the other hand, utilize psychotherapy techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and psychodynamic therapy to help clients explore and address underlying psychological issues.
Conditions Treated
Psychiatrists commonly treat conditions such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, and anxiety disorders that may require medication management. They also work with individuals experiencing severe mental health crises.
Psychologists often work with individuals experiencing stress, grief, relationship issues, and other emotional challenges that can benefit from psychotherapy interventions. They also provide support for individuals coping with trauma, addiction, and eating disorders.
Treatment Modalities

In the field of mental health, both psychiatry and psychology utilize various treatment modalities to help individuals improve their mental well-being. While psychiatrists focus on the medical aspect of mental health, psychologists take a more therapeutic approach to treatment.
Psychiatry Treatment Modalities
- Medication Management: Psychiatrists often prescribe medication to help manage symptoms of mental illnesses such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder.
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): This treatment is used for severe cases of depression or other mental health conditions that have not responded to other interventions.
- Psychotherapy: Some psychiatrists also provide therapy sessions to their patients, combining medication management with talk therapy.
Psychology Treatment Modalities
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Psychologists commonly use CBT to help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Psychoanalysis: This therapy approach focuses on exploring unconscious thoughts and feelings to address underlying issues contributing to mental health concerns.
- Group Therapy: Psychologists may conduct group therapy sessions to provide support and promote social connections among individuals with similar challenges.
Comparison of Therapeutic Techniques
- Psychiatrists primarily rely on medication management to alleviate symptoms, while psychologists focus on psychotherapy and counseling to address underlying issues.
- Psychiatrists may have a more medical approach, working closely with other healthcare providers, while psychologists often collaborate with individuals' support systems to provide holistic care.
- Both professions may use a combination of treatments, tailored to the individual's needs and preferences.
Role of Medication
- Psychiatrists are licensed to prescribe medication, which can play a crucial role in managing symptoms of various mental health conditions.
- Psychologists do not prescribe medication but may work alongside psychiatrists to provide comprehensive care that includes therapy in conjunction with medication management.
- Medication is often used in conjunction with therapy to address both the biological and psychological aspects of mental health concerns.
Training and Specializations
In the fields of psychiatry and psychology, professionals undergo specific training paths to specialize in their respective areas of expertise.The training path for psychiatrists typically involves:
Training Path for Psychiatrists
- Completion of medical school to earn an M.D. or D.O. degree
- Residency training in psychiatry, which typically lasts four years
- Possibility of pursuing fellowships for further specialization in areas such as child and adolescent psychiatry, geriatric psychiatry, addiction psychiatry, etc.
The training path for psychologists usually includes:
Training Path for Psychologists
- Completion of a doctoral program in psychology (Ph.D. or Psy.D.)
- Internship experience in a clinical setting
- Obtaining a state license to practice psychology independently
- Pursuing post-doctoral training or fellowships for specialization in areas such as clinical psychology, counseling psychology, neuropsychology, etc.
Specializations within psychiatry may include:
Specializations in Psychiatry
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Geriatric Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Addiction Psychiatry
- Psychosomatic Medicine
Specializations within psychology may encompass:
Specializations in Psychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- School Psychology
- Industrial-Organizational Psychology
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the comparison between psychiatry and psychology reveals a rich tapestry of specialized knowledge and treatment modalities that cater to diverse mental health needs. By understanding the key differences between these fields, we gain valuable insights into the ways in which professionals in psychiatry and psychology contribute to the well-being of individuals and communities.
FAQ Compilation
What is the main difference between psychiatry and psychology?
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication, while psychologists focus on therapy and counseling without prescribing medication.
What conditions are usually treated by psychiatrists?
Psychiatrists typically treat more severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depression.
What is the training path for becoming a psychologist?
To become a psychologist, one usually needs a doctoral degree in psychology and supervised clinical experience.
How do treatment approaches differ between psychiatrists and psychologists?
Psychiatrists often use a combination of medication and therapy, while psychologists primarily focus on therapy and counseling.

